This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful. See our privacy policy.
EA Bidirectional DC Power Supplies
Programmable power supply & regenerative load all in one
19 Inch Slide-in Housing
(Series PSB and PSB 10000)

Highlights
- Bidirectional
- Autoranging
- Color Touchscreen
Technical Specifications
-
Nominal power
2500W to 30000W
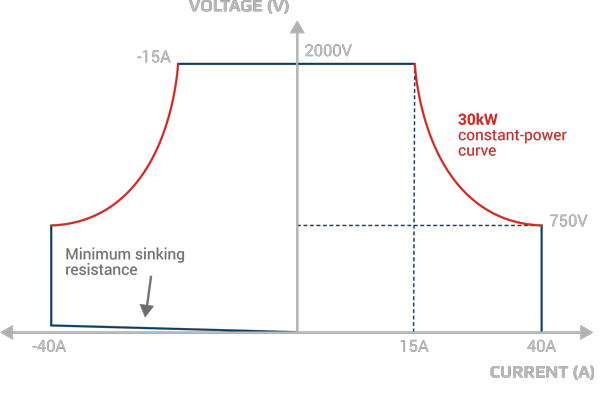
Systems up to 1.92MW parallel operation - Nominal voltage 60V to 2000V
- Nominal current 20A to 1000A
Features
- Master-Auxiliary-Bus for parallel connection
- 19″ Full insertion, 3U or 4U housing
- Analog / USB interface, further options retrofittable
- Microprocessor (FPGA) controlled
- Internal resistance control
- Battery test mode
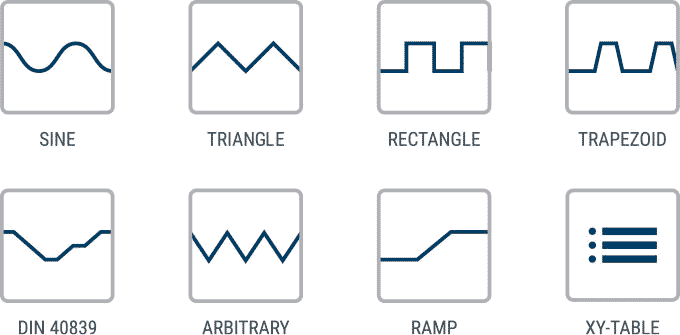
- Arbitrary generator & car startup curve
- Optional: Digital, swappable interface modules
- SCPI and ModBus protocol
- LabView VIs and control software
- High resolution of up to 16 Bit
- Safety compliant to IEC/EN 61010
- EMI compliant to EN 55022 class B
Click below to see our units in 360° view
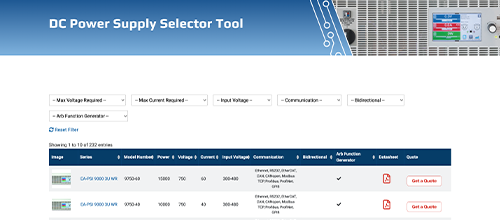
| Series | Power Connection | Voltage | Current | Power | Datasheet | Get Quote |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EA-PSB 10000 3U | 208-480+10 % 3ph | 0-10V to 0-2000V | 0-20A to 0-510A | 5 kW / 10 kW / 15 kW | Get a Quote | |
| EA-PSB 10000 2U | 100-240+10 % 1ph | 0-10V to 0-1500V | 0-6A to 0-120A | 600-3000W | Get a Quote | |
| EA-PSB 10000 4U | 208-480+10 % 3ph | 0-10V to 0-2000V | +-0-40A to 0-1000A | 30kW | Get a Quote | |
| EA-PSB 9000 3U (EOL) | 380-480V~ 3ph L-L | 0-60V to 0-1500V | +-0-20A to +-0-360A | 5000-15000W | Get a Quote | |
| EA-PSB 9000 3U 208V (EOL) | 220-240V~ | 0-60V to 0-750V | +-0-20A to +-0-120A | 2500W | Get a Quote |
Find the Right Tool

Power Selection Guide
What MUST you consider when choosing a Programmable DC Power Supply? What output is right for your application? How much power you you pay for without over specifying? Download our Guide to help you navigate the many considerations when specing the right DC power supply.
Download Power Guide
FAQs
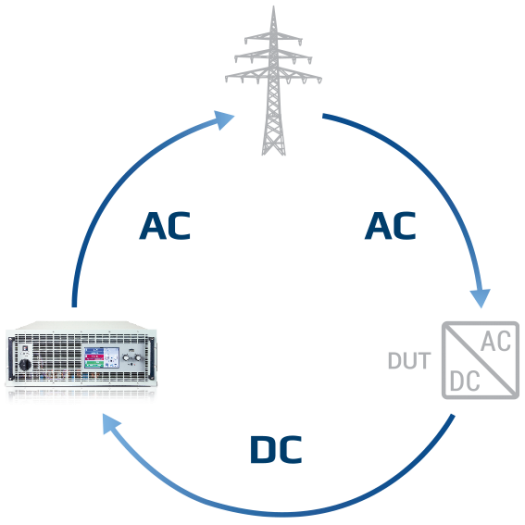
A bidirectional power supply is used to provide and absorb the flow of electrical energy in both directions. For example, it can supply electrical energy to a device or circuit and absorb electrical energy from it. In this case, it acts as a “sink” to absorb excess energy, convert it back to usable form, and manage power flow efficiently.
A bidirectional power supply is often used in constant voltage (CV) or constant current (CC) mode to simulate a rechargeable battery for a device under test (DUT). A bidirectional power supply then acts as a versatile tool to test and evaluate electronic devices, as it allows engineers to better understand how a device or circuit will operate through voltage fluctuations or below its nominal operating current.
A unidirectional power supply can provide only electrical energy in one direction, typically from the source to the load. In contrast, a bidirectional power supply can both provide and absorb electrical energy in two directions, allowing for greater versatility, especially for a device under test.
A bidirectional converter efficiently converts and controls electrical power between two different forms or directions, such as DC to AC or AC to DC. It can reverse the power flow as needed. The primary purpose of a bidirectional converter is to manage power flow, and this enables applications such as energy storage.
A bidirectional DC power supply can act as either a source of electricity or a sink for electricity. This means it can deliver electricity to a connected device or circuit. It can also act as a power sink, absorbing electrical energy from a connected device or circuit. Acting as a sink, a bidirectional power supply can effectively consume this excess energy, either returning it to the local grid/building facility in a regenerative system or dissipating excess energy in the form of heat.
A bidirectional power supply can reverse or control the flow, making it useful in myriad applications such as battery testing, regenerative braking systems in electric vehicles or renewable energy systems, to name a few. For example, a bidirectional DC power supply allows for research, testing and other industrial applications that would benefit from the ability to control and reverse the power flow.
A DC-DC converter can either be designed as unidirectional or bidirectional. As the prefix indicates, a unidirectional device or converter would allow current flow in a single direction. In contrast, a bidirectional DC-DC converter will allow the current to flow in both directions.
A bidirectional DC-DC converter can manage power flow in both directions, lending it added versatility compared to a unidirectional DC-DC converter. This capability makes it a useful tool for research, testing and measurement in applications requiring power to be supplied and extracted from the same device, such as energy exchange between batteries and the grid. The energy exchange between sources and loads can improve overall system efficiency by optimizing energy utilization.